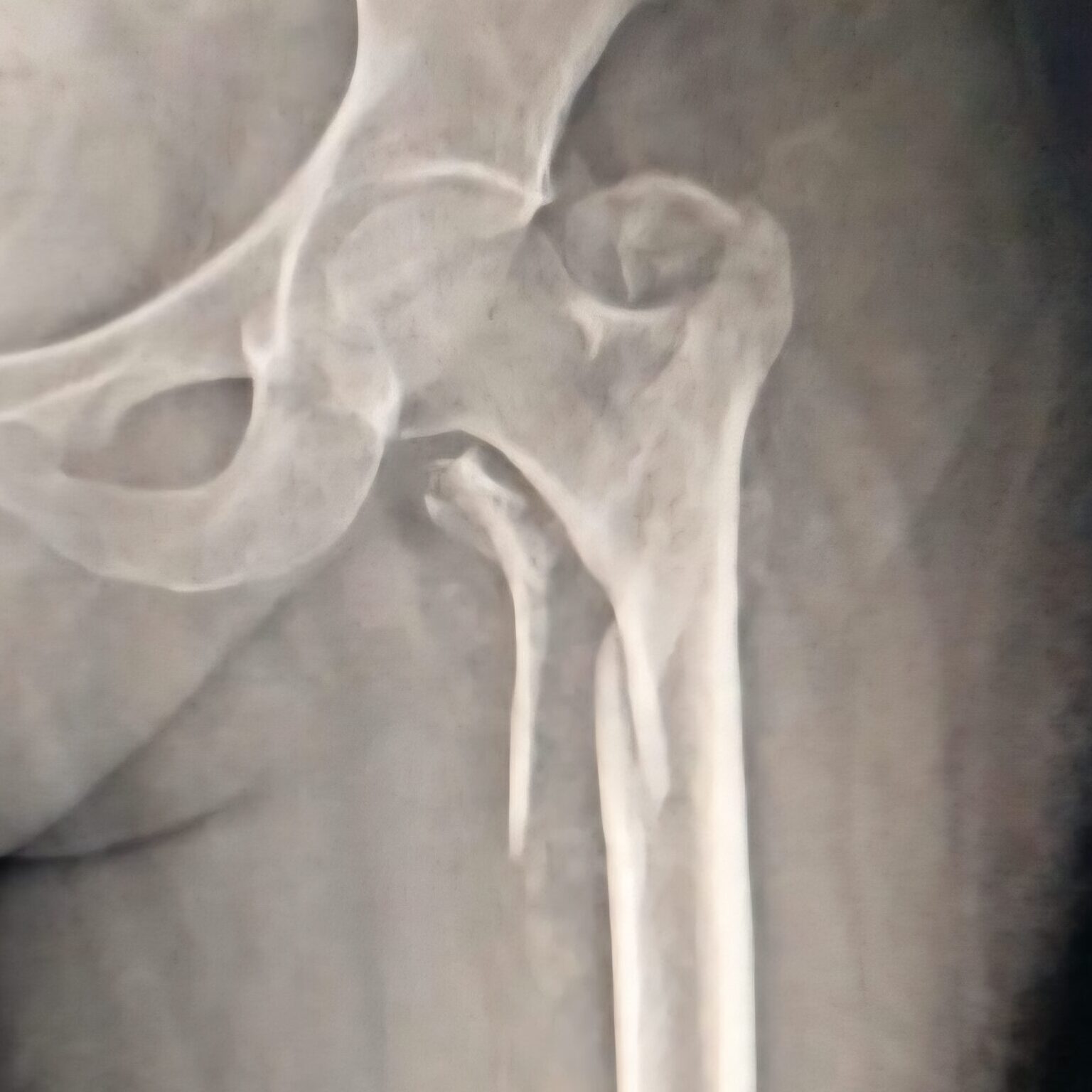
A 4-part hip fracture is a serious type of injury, commonly affecting older adults, especially those with weak bones due to osteoporosis. It involves a break in the proximal femur (thigh bone), specifically affecting four key segments of the bone near the hip joint. As an orthopedic surgeon in Indore specializing in trauma and joint surgeries, I have treated many such cases with successful outcomes. This page is dedicated to helping patients and caregivers understand this injury better.
What Is a 4-Part Hip Fracture?
The hip joint is a ball-and-socket joint, where the femoral head (the ball) fits into the acetabulum (the socket) of the pelvis. The proximal femur consists of:
- Femoral head
- Femoral neck
- Greater trochanter
- Lesser trochanter
A 4-part fracture involves separation or breakage in all four of these components. It is classified under Neer’s classification, commonly used for proximal femur fractures, though originally applied to shoulder injuries.
This type of fracture is unstable and complex, often requiring surgical intervention for optimal recovery.
Causes of 4-Part Hip Fracture
In my clinical experience, the most common causes include:
- Falls – Especially among the elderly due to poor balance or weak bones.
- High-impact trauma – Such as road traffic accidents or falls from height in younger patients.
- Osteoporosis – Reduced bone density increases fracture risk.
- Overuse or stress – Rarely, repetitive stress can contribute to fracture in compromised bones.
Symptoms
The hallmark signs and symptoms of a 4-part hip fracture include:
- Severe hip or groin pain
- Inability to bear weight on the leg
- Shortened and externally rotated leg (leg appears twisted outward)
- Swelling or bruising around the hip
- Stiffness and immobility
If you or someone you know experiences these symptoms after a fall or accident, seek immediate orthopedic evaluation.
Diagnosis
In my Indore clinic, diagnosis starts with a thorough clinical examination, followed by:
- X-rays – The first-line imaging to identify the fracture.
- CT Scan – Provides a 3D view of the hip, essential in complex or displaced fractures.
- Bone Density Test (DEXA) – To assess underlying osteoporosis.
Accurate diagnosis is crucial to plan the appropriate treatment.
Treatment Options
Due to the complexity of 4-part fractures, non-surgical management is rarely recommended. The mainstay of treatment is surgical intervention, depending on the patient’s age, bone quality, and overall health.
1. Hemiarthroplasty or Total Hip Replacement
In most elderly patients, I recommend hip replacement surgery. The damaged ball and possibly the socket are replaced with artificial components.
- Hemiarthroplasty – Only the femoral head is replaced.
- Total Hip Replacement (THR) – Both the ball and socket are replaced, especially if the socket is also damaged or arthritic.
2. Internal Fixation
For younger patients with good bone quality, preserving the native hip is preferred. I use surgical screws, plates, or intramedullary nails to fix the fracture.
This is more technically demanding and needs careful post-op monitoring, but can offer good outcomes.
Recovery & Rehabilitation
Recovery after a 4-part hip fracture surgery typically involves:
Hospital Stay
- Most patients stay for 3–5 days post-surgery.
- Early mobilization is encouraged to reduce complications like clots or bed sores.
Physiotherapy
- Begins as early as Day 1 after surgery.
- Focuses on strengthening, range of motion, and eventually walking with support.
Medications
- Pain management, antibiotics, and anti-osteoporotic drugs as needed.
- Anticoagulants to prevent blood clots.
Follow-up
- Regular X-rays to monitor healing.
- Stitch removal around Day 14.
Full recovery may take 8–12 weeks, depending on age, surgery type, and physical therapy adherence.
Risks and Complications
As with any surgery, certain risks are involved:
- Infection
- Dislocation of the prosthesis
- Blood clots
- Implant loosening or wear over time
However, with meticulous surgical technique and proper rehabilitation, the risk is minimal. I ensure my patients are well-informed and prepared at every step.
Prevention Tips
While not all fractures can be avoided, certain steps help reduce risk:
- Regular exercise to improve strength and balance
- Bone health checks (DEXA scans for osteoporosis)
- Vitamin D and calcium supplements
- Fall-proofing your home – Use railings, anti-slip mats, and proper lighting
- Avoiding over-sedating medications in the elderly
When to See an Orthopedic Surgeon?
If you or a loved one has suffered a fall and complains of hip pain, especially with leg deformity or inability to walk, consult an orthopedic specialist immediately. Early intervention leads to better outcomes.
Why Choose Dr. Anupam Khandelwal in Indore?
With years of experience in treating complex hip fractures, including 4-part fractures, I offer:
- Advanced surgical care including minimally invasive techniques
- Personalized treatment plans
- Modern physiotherapy support
- High success rate with fast recovery
Located in Indore, I am dedicated to providing compassionate, evidence-based orthopedic care.
If you have any questions or wish to book a consultation, feel free to contact my clinic.